Toothbrush tester for bristle stiffness and pull-out resistance

Solution
- Motorised tensile test stand
- Custom grips to suit the each individual test requirement
- Graphing software
Benefits
- Single testing station for multiple tests
- Soft, medium, firm grading quantified
- Data capture and results comparable to international test standards
- System usable by production staff in the factory environment with maximum reproducibility
Requirement
Toothbrushes are just as important as toothpaste for ensuring effective oral hygiene. As consumers we often underestimate the essential role they play in removing food particles, getting rid of plaque and stimulating the gums. But toothbrush manufacturers are hard at work to keep us happy by implementing numerous functional and aesthetic improvements to the heads and bodies of their products. Everything from introducing digital displays to tell us the date we should change the toothbrush, right through to sculpted longer handles for a more comfortable grip and extended reach.
Before these products can hit the shelves however, they need to be thoroughly tested to make sure they comply with the appropriate ISO standards.
ISO 22254 covers manual toothbrushes and is a useful test method to assess the stiffness of the bristles.
ISO 20126 covers manual toothbrushes and ISO 20127 covers powered toothbrushes. They describe methods for measuring the tuft retention strength.
ISO 16049 covers specialist small brushes designed to clean between teeth and long enough to access hard-to-reach areas of the mouth. They are known as ‘interdental brushes’. It includes a test methodto make sure that the stem of the brush does not separate from the handle when used.
A leading manufacturer of manual toothbrushes consulted Mecmesin to source a multi-purpose testing system which could meet the specific demands of a number of ISO test standards. The primary requirement was to measure the tensile and compressive strength characteristics of the brushes and handles.
Each test required different grips, and the equipment needed to be robust and simple to operate for production staff in a factory environment. It was important for Mecmesin to find a solution involving test equipment requiring the minimum of ‘set-up’ time.
Solution
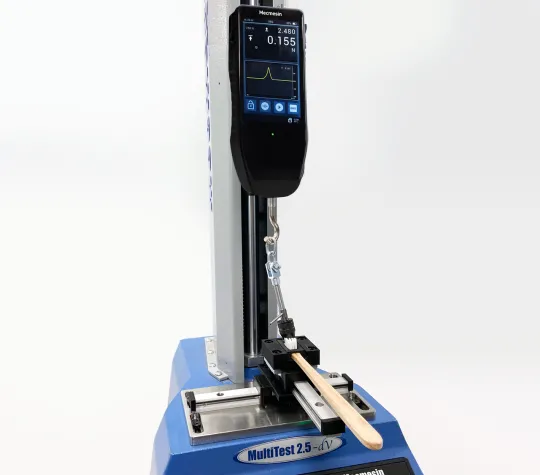
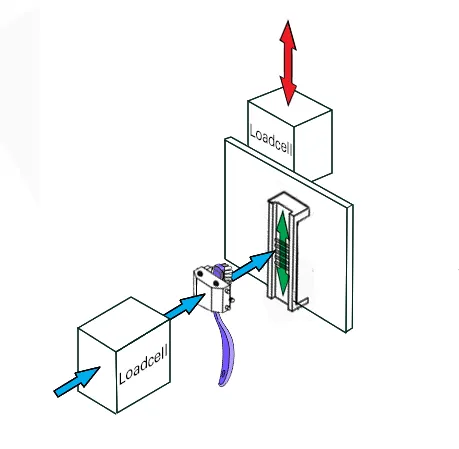
A motorised test stand fitted with a digital force gauge adapted with grips, accessories and sensors was used to perform the tests. Dedicated holders for differing shapes of toothbrush head were produced, which easily sotted into clamping fixtures.
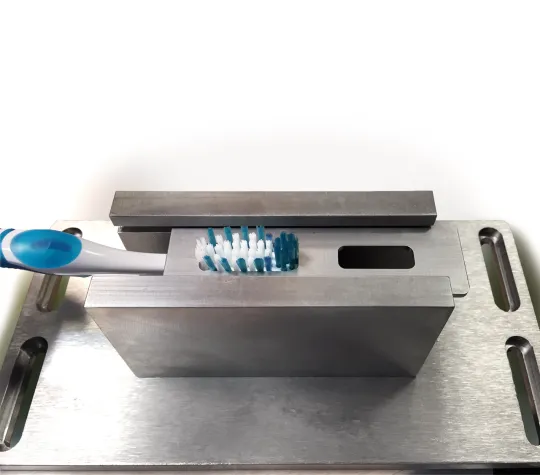
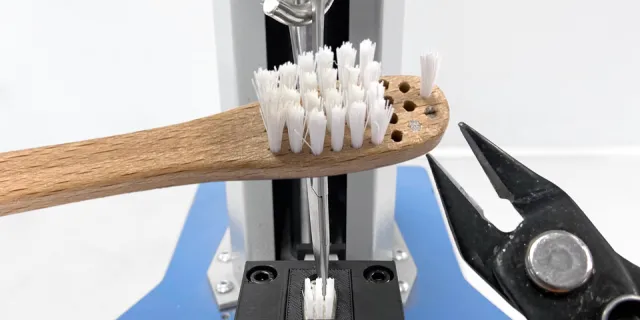
- ISO 22254 - Bristle Stiffness Fixture including additional loadcell and display for monitoring 5N pre-load force.
It measures the resistance of the tufted filaments to deflection – put simply the bristles are wetted and then pushed against a metal grid with 5N pre-load to mimic the pressure we apply when brushing our teeth. They are then pulled backwards and forwards at a constant speed of 600mm/min for 5 times over the grid and the maximum force is recorded for each direction. The max force is then divided by the area of the tufted portion to obtain a stiffness value in N/cm².
- ISO 20126 and ISO 20127 - Tuft Retention Fixture.
Both describe the test method to make sure the filaments of the brush do not break or detach too easily. Known as the ‘tuft retention test’ it measures the maximum force required to pull out a single tuft of filaments from the head of the brush at a constant speed of 20mm/min. The max force for tuft removal should be no lower than 15N.
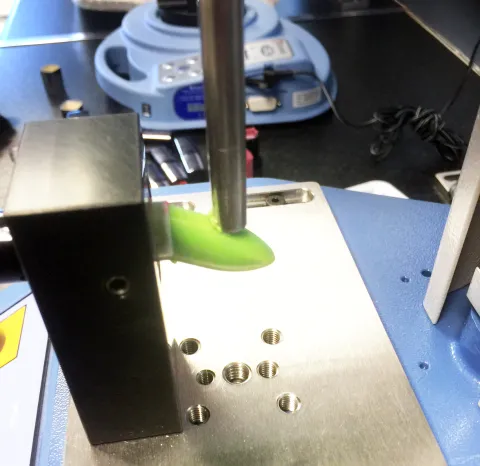
- ISO 16409 - Stem to Handle Retention Fixture.
The test method requires the handle to be clamped and pulled at a constant speed of 20mm/min against a retaining plate until the stem detaches. The stem retention force shall be at least 15N.
Test equipment
- MultiTest Motorised Test Stand
- Advanced Force Gauge 100 N
- 50N Smart S-Beam loadcell and AFTI display
- Specialist fixtures according to ISO standards
- Emperor-Lite graphing software